5 major 3D printing technology for turn metal into parts
| 3D printing is usually realized by digital technology material printer. Metal 3D printing technology can be directly used for rapid prototyping of metal parts. It has broad industrial application prospects and is the world’s key 3D printing technology. Let’s take a look at the five metal 3D printing principles of NPJ, SLM, SLS, LMD and EBM. |

1.SLM(Selective Laser Melting).
SLM is the laser fusion forming technology of the selected area. It is the most common technology in metal 3D printing. It uses the fine focus spot to quickly melt the preset metal powder, and directly obtains any shape and parts with complete metallurgical bonding. More than 99%. . SLM technology overcomes the complexity of the process of manufacturing metal parts with Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) technology.
Laser galvanometer system is one of the key technologies of SLM. The following is the working diagram of galvanometer system of SLM Solution:
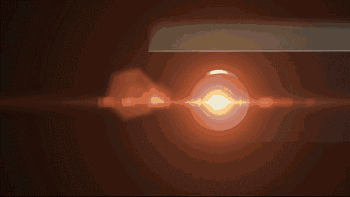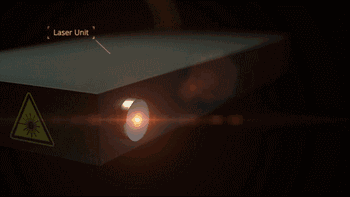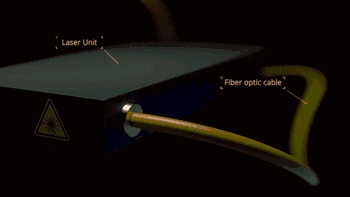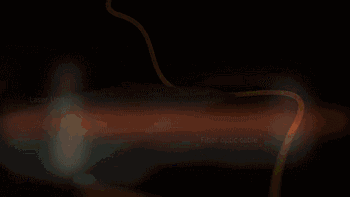 |
 |
| Laser galvanometer | Laser emission |
 |
 |
| Laser transmission | Scanning galvanometer |
Metal powder melting process
In the metal 3D printing process, since the parts are usually complicated, it is necessary to print the supporting material, and the support needs to be removed after the finished part is finished, and the surface of the part is processed.
 |
 |
| Printing support material | Take out the parts |
 |
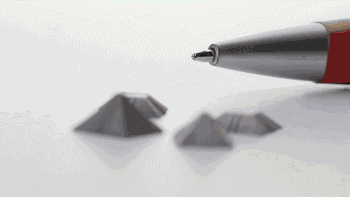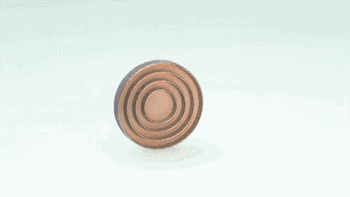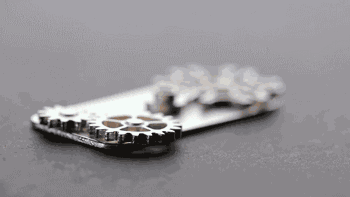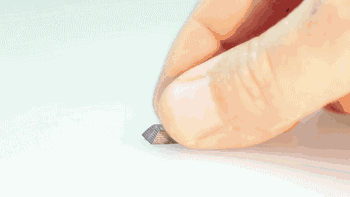 |
| Metal grain refinement | Liquid phase discharge process |
2.SLS(Selective Laser Sintering)
SLS is the laser sintering forming technology of the selected area, which is similar to the SLM technology. The difference is that the laser power is different, and it is usually used for 3D printing of high molecular polymers.
The following is the process by which SLS prepares plastic parts:
 |
 |
| SLS preparation of plastic parts | Model layered slice |
 |
 |
| Get parts | Post processing |
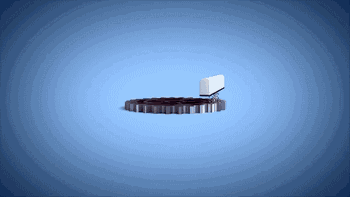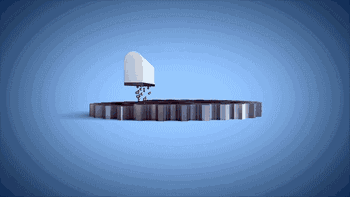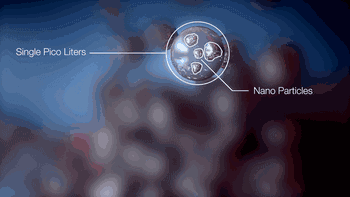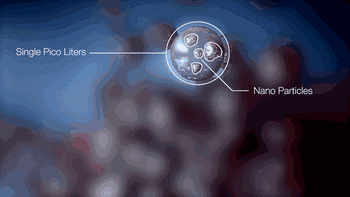
3.NPJ(Nano Particle Jetting)
NPJ technology is the latest metal 3D printing technology developed by Israeli company Xjet. Compared with ordinary laser 3D printing, it uses nano liquid metal and is deposited by inkjet. The printing speed is faster than ordinary laser printing. Double, and has excellent precision and surface roughness.
4.LMD(Laser Metal Deposition)
LMD is a laser cladding molding technology. The technology has many names. Different research institutes independently research and independently name them. The commonly used names include: LENS, DMD, DLF, LRF, etc. The biggest difference from SLM is that the powder collects through the nozzle to work. The table top, with the laser light at a point, the powder melts and cools to obtain a stacked cladding entity.
The following is the working process of LENS technology:
 |
||
| Construction process |
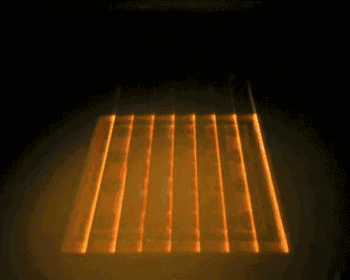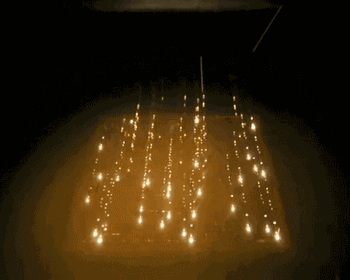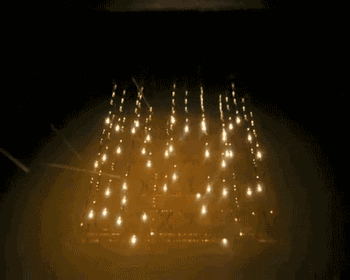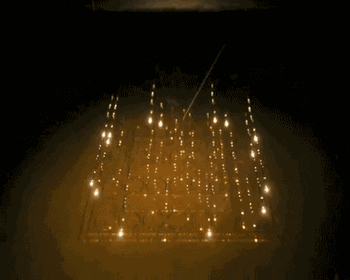
5.EBM(Electron Beam Melting)
EBM is an electron beam melting technology, and its process is very similar to that of SLM. The difference is that the energy source used by EBM is an electron beam. The EBM’s electron beam output energy is usually an order of magnitude larger than the SLM’s laser output power, and the scanning speed is much higher than that of the SLM. Therefore, during the construction process, the EBM needs to preheat the entire molding platform to prevent the temperature from being too large during the molding process. Come to a large residual stress.
The following is the EBM work process:
| |
 |
|
| |
EBM work overall warm-up |
|
Link to this article: 5 major 3D printing technology for turn metal into parts
Reprint Statement: If there are no special instructions, all articles on this site are original. Please indicate the source for reprinting:https://www.cncmachiningptj.com/,thanks!
Link to this article:5 major 3D printing technology for turn metal into parts
Reprint Statement: If there are no special instructions, all articles on this site are original. Please indicate the source for reprinting:Alloy Wiki,thanks!^^







